Process:
The Continuous Filament Winding Process is the manufacturing of GRP pipes from continuously flowing glass fiber by winding it on an automatic machine.
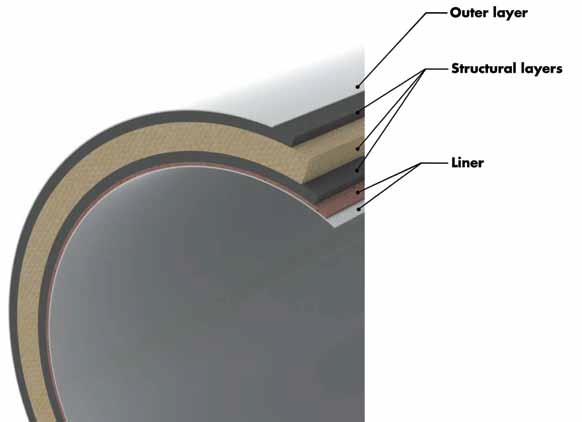
The inner and outer walls of the pipe are constructed by pressing glass fiber and resin together, and filling material (sand) is then added.
As a result of reinforcing a high ratio of polyester by glass fiber, the inner and outer surfaces of the pipe become extremely robust against chemicals.
Since the mid-section of the pipe is highly durable, the required stiffness is obtained, and the resistance against working pressures is obtained throughout the length of the pipe.
Material:
Standard RUSELBORU GRP pipes are manufactured using orthophthalic or terephthalic unsaturated polyester resin. In the case of special design requirements to meet specific conditions of the project, it is possible to manufacture using isophthalic and vinyl ester resin too.
Manufacturing:
The main machine in the Continuous Filament Winding manufacturing process comprises of a continuous steel band supported by beams that form a cylindrical mandrel.
By the motion of the mandrel under the control of the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) and the computers(PC), the glass fiber, the resin, the filling material and the surface materials are applied by precision measurements. The PLC-PC modules provide an integrated process control in line with the pre-programmed designs. Basic data, such as diameter, stiffness and pressure class are entered into the program. The PC calculates all the setting values of the machine. The process parameters and the thickness of the pipe are continuously monitored and traceability is provided by storing these data.
Curing of the laminate develops depending on the heat. Direct heating of the laminate is ensured by heating elements. Laminate temperature is measured on the cure region from various points. Temperature distribution is monitored on the PC monitor graphically.
Extraction of resin is administered from two different lines. Special resin for the inner layer of the pipe can be used for highly corrosive applications, while a normal resin for the body and outer layer can be utilized.
A cutting unit compatible with the pipe, which has an axial and radial stroke, enables the pipe to be cut smoothly and perpendicularly. Cutting operations take place automatically by entering the length of the pipe into the control system.
Pipes that have been cut are transferred to specifically designed lifting stands, then to the chamfering and calibration section, and from there to hydrostatic test section.